The body can be divided on the basis of the parts that need cleansing. Head, GIT (gastro- intestinal system), upper and lower. The five main Karmas to cleanse the complete body are
Five Karmas
Vamanam
(therapeutic emesis)
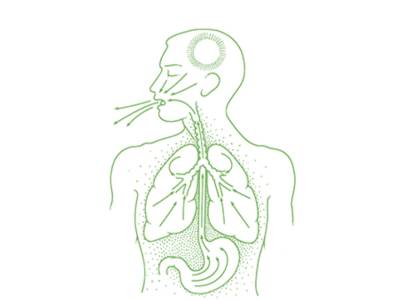
Induced vomiting helps clear the upper gastro till the duodenum (end of stomach) and part of the respiratory tract.
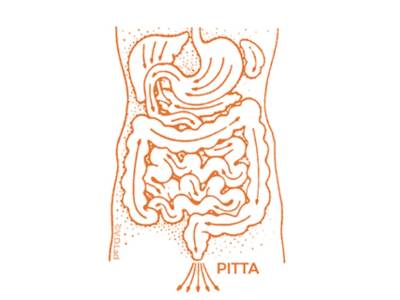
Virechanam
(purgation)
Induced purgation clears the lower gastro from the duodenum (end of stomach) till the exit.
Anuvasana
(enema using medicated oil)
Oil enema helps lubricate the rectal area and take out all the lipid soluble waste out through the anus.
Nasyam
Nasal instillation of medicated substances helps clear the respiratory tract and para-nasal sinuses.
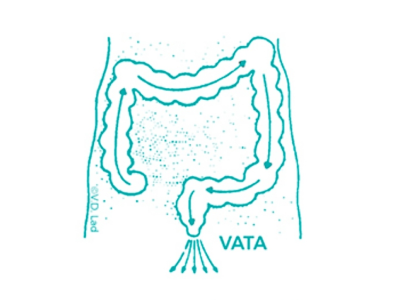
Astapana Vasti (Therapeutic Decoction Enema)
Decoction enema cleanses the area from the transverse colon till the anus.
Vaman
Vaman is one of the five therapies of panchakarma in Ayurveda. Vaman means therapeutic vomiting which is a medicated emesis.
Virechan
Virechana therapy is an effective Ayurvedic treatment that can cure a number of health problems naturally.
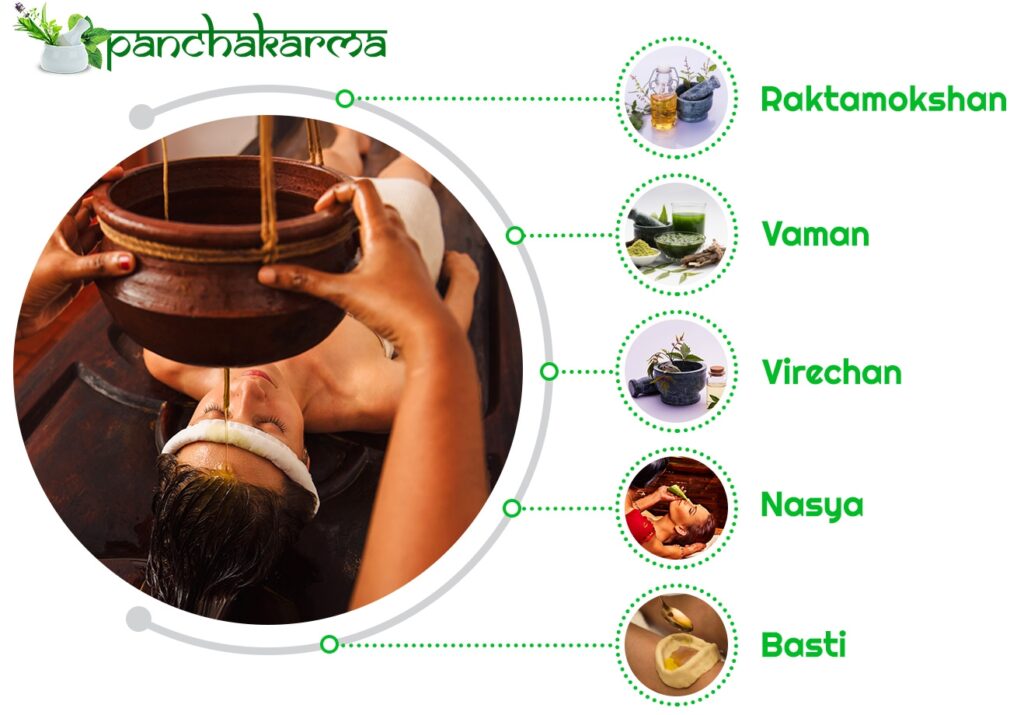
Basti
Basti is often administered in two stages: an oil stage and a decoction stage. In the first stage,
Steps followed
The complete process of Panchakarma consists of three steps.
Poorva Karma
Which is the preparatory procedure required before the main procedure to enable a person to receive the full benefits of the main treatment. It consists of two main processes – Snehan (oleation) and Swedan (fomentation). These methods help to dislodge the accumulated poisonous substances in the body, thus preparing them for their complete removal.
Pradhan Karma
Pradhan Karma or the main procedure. On completion of the first step, it is decided which of these are to be done depending upon the proximity of the waste. An increased level of upper respiratory tract waste shall call for Vamana. Similarly, a lower gastro accumulation of waste calls for a Virechanam.
Paschaat Karma
Paschaat Karma or the post-therapy dietary regimen to restore the body’s digestive and absorptive capacity to its normal state.
